Getting to Know Plants is Chapter 7 taken from JKBOSE Class 6 Science. The given post is about the chapter Getting to Know Plants Class 6th Question Answers. You will get short notes and question answers in the chapter in this post. The previous post was about Chapter 6 Changes Around Us Question Answers. Let’s begin:

Getting to Know Plants Class 6th Question Answers
Overview of Chapter
- HERBS, SHRUBS AND TREES.
- STEM.
- LEAF.
- ROOT.
- FLOWER.
There is a large number of plants growing on earth. They are living entities which are different from animals because they remain fixed in soil with help of their roots. Most of the green plants on earth are grouped into three categories: herbs, shrubs, and trees based on their life span, size and nature of stem.
- HERBS, SHRUBS AND TREES: The small plants with green soft and delicate stems are called herbs. They have a non-woody stem, a short life span and an average height of less than one metre. For example, Tomato, Radish, Wheat, Paddy, Cabbage etc.
Medium-sized plants with thick, hard and woody stems and branching at the base of the plants are called shrubs. The plants have a bushy appearance and have a life span of many years but less than that of trees. For example, Rose, Croton, China Rose etc.
The tall and big plants having thick and woody stems are called trees. The trees have one main stem called a trunk. The branches of a tree appear higher up on the stem much above the ground. For example, Neem, Mango, Pine, Coconut, Banyan etc.
There are plants which are different from herbs, shrubs and trees. These are climbers and creepers.
Climbers: The plants having thin, long and weak stems which cannot stand upright without any support are called climbers. For example, bitter gourd, grapevine, pea plant etc.
Creepers: The plants having thin, long and weak stems which cannot stand upright and spread on the ground are called creepers. For example, strawberries, pumpkin and watermelon etc.
- STEM: The part of a plant which is above the ground and has branches, leaves, flowers and fruits is called a stem. The main functions of the stem are:
- It holds the plant upright.
- It carries water and minerals from the roots to the leaves and other parts of a plant.
- It carries food from leaves to other parts of a plant.
- LEAF: The thin, broad, flat and green part of a plant which is attached to the stem is called a leaf. A leaf consists of two parts: lamina and petiole. The broad, green flattened part of the leaf is called the lamina. The thin stalk with which a leaf is attached to the stem or branch is called a petiole. The leaves have three main functions:
- Leaves are food factories of the plant.
- The leaves get rid of excess water from the plant through transpiration.
- The leaves carry out the process of respiration in plants.
- ROOT: The part of a plant which is below the ground is called root. There are two main types of roots – Tap roots and Fibrous roots. The roots of plants perform these functions:
- Root anchor the plant to the soil.
- Roots absorb water and minerals from the soil.
- Roots help in holding the soil together.
- FLOWER: The flower is the reproductive part of the plant. The main parts of a flower are sepals, petals, stamens and pistils. The main function of flowers is to produce seeds and fruits.
Getting to Know Plants Class 6 Questions
Exercises:
- Correct the following statements and rewrite them in your notebook.
(a) Stem absorbs water and minerals from the soil.
(b) Leaves hold the plant upright.
(c) Roots conduct water to the leaves.
(d) The number of petals and sepals in a flower is always equal.
(e) If the sepals of a flower are joined together, its petals are also joined together.
(f) If the petals of a flower are joined together, then the pistil is joined to the petal.
Ans. Here are the correct statements:
(a) Roots absorb water and minerals from the soil.
(b) Stem holds the plant upright.
(c) Stem conducts water to the leaves.
(d) The number of petals and sepals in a flower is not always equal.
(e) If the sepals of a flower are joined together, its petals may or may not be joined together.
(f) If the petals of a flower are joined together, then the pistil may or may not be joined to the petal.
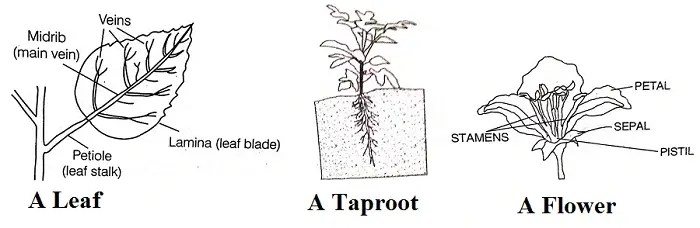
- Draw (a) a leaf, (b) a taproot and (c) a flower, which you have studied for Table 7.3.
Ans.
3. Can you find a plant in your house or in your neighbourhood, which has a long but weak stem? Write its name. In which category would you classify it?
Ans. Yes, there are several plants like money plants, grapevine, and gourd plants which have weak stems. These can be classified as creepers and climbers.
4. What is the function of a stem in a plant?
Ans. The following are the main functions of a stem in a plant:
a) Stem conducts water from the roots to the leaves of a plant.
b) Roots provide support to the plant.
c) Stem conducts food from leaves to other parts of a plant.
d) Stem bears leaves, flowers and fruits.
5. Which of the following leaves have reticulate venation?
Wheat, tulsi, maize, grass, coriander (dhania), China rose
Ans. The leaves of tulsi, coriander and China Rose have reticulate venation.
6. If a plant has fibrous roots, what type of venation do its leaves likely to have?
Ans. If a plant has fibrous roots, its leaves have parallel venation.
7. If a plant has leaves with reticulate venation, what kind of roots will it have?
Ans. If a plant has leaves with reticulate venation, it will have tap roots.
8. Is it possible for you to recognize the leaves without seeing them? How?
Ans. Yes, it is possible to recognize the leaves without seeing them by touching them or feeling them because the leaves having reticulate venation have a broad midrib while leaves having parallel venation has no midrib.
9. Write the names of the parts of a flower.
Ans. The various parts of a flower are 1) Sepals 2) Petals 3) Pistil 4) Stamens
10. Which of the following plants have you seen? Of those that you have seen, which one has flowers?
Grass, maize, wheat, chilli, tomato, tulsi, pipal, shisham, banyan, mango, jamun, guava, pomegranate, papaya, banana, lemon, sugarcane, potato, and groundnut.
Ans. We have seen all these plants. Plants with flowers are:
Chilli, Jamun, Tomato, Guava, Tulsi, Pomegranate, Mango, Papaya, Lemon, Banana.
11. Name the part of the plant which produces its food. Name this process.
Ans. The part of a plant which produces its food is a leaf. The process of preparation of food by plants is called photosynthesis.
12. In which part of a flower, you are likely to find the ovary?
Ans. The ovary is found in the lowermost swollen part of the pistil in a flower.
13. Name two flowers, each with joined and separated sepals.
Ans. Flowers having joined leaves: Cotton, Tomato, Datura.
A flower having separated leaves: China rose, Mustard flower, Lotus, Lily Jasmine.
14. a. Give the technical names of I. Baby root, II. Baby shoot.
b. Name two roots modified for storage of food.
c. Sweet potato is _________ and potato is a ______.
d. What is a hermaphrodite flower?
Ans. a) The technical name for baby root is a radicle
The technical name for a baby shoot is plumule.
b) The two roots which are modified for storage of food are carrot, radish and sweet potato.
c) Sweet potato is a root and potato is a stem.
d) A flower which bears both males (stamen) and females part (pistil) is called a hermaphrodite flower.
15. Multiple Choice Questions:
a. Which of the following has a taproot?
i. Maize
ii. Wheat
iii. Pea
iv. Rice
Ans. iii) Pea
b. Which of the following is a modified stem?
i. Radish
ii. Onion
iii. Sweet potato
iv. maize
Ans. ii) Onion
c. Pollen grains are produced in
i. Flowers
ii. Ovary
iii. Anther
iv. Fruit
Ans. Anther
Leave a Reply