“Rocks and Minerals” is Chapter 8 from Let’s Look Around and Learn EVS for Class 5th for students of JKBOSE. You have already been provided with Question Answers of Chapter Rocks and Minerals in the previous post. This post is specifically about Rocks and Minerals Class 5 EVS Chapter Notes. Let’s not waste time and dive deeper:

Rocks and Minerals Class 5 EVS Chapter Notes
Introduction
The chapter “Rocks and Minerals” details children about different types of rocks and minerals, how are they and what are their uses. The chapter aims to provide basic knowledge about rocks and minerals to young kinds.
Rocks and Minerals Chapter Notes
The surface of the earth that we walk on, construct buildings and grow gardens on is made up of rocks. All the rocks in the world are made up of chemicals called minerals Granite, sandstone, chalk, marble and slate are all different types of rocks. The pebbles that we see on the beach are worn down and smoothed rocks by the action of the sea. The stones that are used to build structures from small cottages to magnificent cathedrals are rocks. All rocks are not hard. Clay is a type of soft rock.
What is Rock?
A rock may be defined as any natural mass of mineral matter that makes up the earth’s crust.
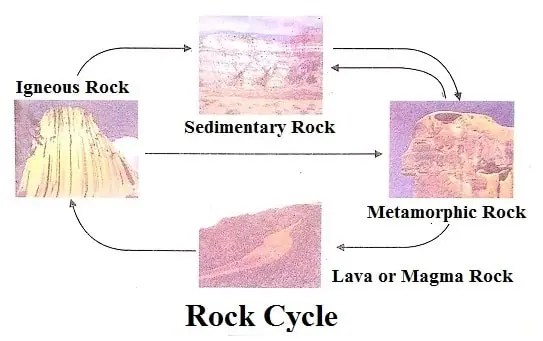
Types of Rocks
There are three main types of rocks:
- Igneous
- Sedimentary
- Metamorphic.
Igneous rocks
The term “Igneous” means fire-formed. There is a fiery hot substance inside the earth is called magma. This magma comes out of the earth by rupturing the earth’s surface forming a volcano. In a volcano, the magma pours out in a molten stream. This molten magma on cooling solidifies to form a rock. Such rocks which are formed from fiery-hot magma are called igneous rocks.

Magma is a mixture of different minerals. These minerals occur in different proportions. So, igneous rocks contain different minerals. Such as granite and basalt.
Composition of Igneous Rocks
Granite: Granite is intrusive igneous rock. Intrusive rocks are formed from magma that cools and solidify within the crust of the planet. There are several types of granite, but all are light coloured because of the light-coloured minerals within them. Granite is formed when Magma cools slowly under the surface of the Earth. Many temples in South India have been made of granite.
Basalt: Basalt is a typical extrusive igneous rock formed from lava. Extrusive rocks are formed on the surface of the Earth from magma that has emerged from underground. It is dense and dark because of the minerals it contains. It is fine-grained because of its quick cooling. Igneous rocks tend to be very hard. When broken up, they make a good, strong road surfacing material, especially when coated with tar.

Sedimentary rocks
Sedimentary rocks are formed from igneous rocks when they are slowly broken down by wind, rain and water into tiny bits. Rivers carry these tiny bits of rocks into the sea where this rocky material along with seashells and skeletons of tiny sea animals settles at the bottom of the sea. These materials are called sediments.
With the passage of time, new layers are laid over the old ones. The weight of the seawater and top layers squeezes the layers at the bottom into solid rocks. Such rocks are called sedimentary rocks.

Sandstone, limestone, shale and rock salt are examples of sedimentary rocks. Chalk is also a sedimentary rock. It is soft limestone.
Sandstone: Sandstone is made from layers of sand in deserts, or on sea beaches, which have been naturally cemented together. The red rock of Devon, England is a typical sandstone. Sandstones are commonly used as a building material. The Red Forts at Delhi and Agra are made up of red sandstone. Sandstone consists mostly of a mineral called quartz. Many buildings in Jaipur are built of sandstones and so Jaipur is also known as Pink City. Sandstone is made from particles of send that get cemented together.

Limestone: Limestone is a biogenic rock. It is made up of living materials. The shelly limestone is made up of broken seashells. Other examples of biogenic sedimentary rocks are reef limestone and coal. Limestone is also hard rock and is, commonly, used as a building material.
Shale: Shale is formed of compressed mud, silt and clay, mostly due to pressure. Shale rock is made up of parallel layers which readily split into pieces.

Rock Salt: Seawater contains dissolved minerals. When an area of sea dries out, these minerals are deposited as a layer at the bottom. Rock salt is a typical chemical sedimentary rock.
Chalk: Chalk is made up of millions of tiny calcium carbonate (lime) skeletons.
Metamorphic Rocks
Metamorphic rocks are changed rocks. The intense heat and pressure inside the earth change the igneous and sedimentary rocks into metamorphic rocks. Metamorphosis means change. The characteristics of the changed rock are different from the parent rock due to the changes in the mineral contents of the rock. Shale and marble are the main examples of metamorphic rocks. Gneiss and coal are other examples of metamorphic rocks.
Slate: Slate is a dark grey and shiny rock. It is formed by the metamorphosis of shale. It splits easily into thin slices. Slate is used as a roofing material and a chalkboard surface.
Marble: Marble is a type of thermal metamorphic rock, formed when heat is applied to limestone. It is a smooth rock. It is an attractive building and sculpting material. It is also used in making statues, tabletops and various other items. Its colour can vary from white to white streaked with brown, red, green or grey.

Coal is used as a fuel in powerhouses to produce electricity, in the extraction of iron and many refineries. Coal gives us many useful products such as coal tar, coal gas, ammonia and coke. Coal tar is used for constructing roads.
Minerals
Minerals are the building blocks of rocks. All the rocks, igneous, sedimentary or metamorphic, are composed of minerals. A mineral is a chemical compound that occurs naturally. Each different mineral is made up of crystals of a particular chemical. Minerals can be identified by their hardness, colour, the way they reflect light, the way they break and their density.
Minerals making up igneous rocks include quartz, plagioclase and olivine. Augite is found in metamorphic rocks. Dolomite makes up limestone sedimentary rocks. Quartz is a very common mineral.
How Minerals are Formed?
All minerals are originally formed from hot magma. When the magma cools, crystals of minerals appear. These crystals first may sink in the magma so that the composition of the magma changes with depth. Thus, a sequence of minerals is formed in the rocks as the magma cools. Lighter minerals occur above the denser minerals. If the crystals form slowly, they may form gemstones.
Ores and Gemstones
Many useful metals are found in rock or mixed with loose rock materials. Such mixtures are called metallic ores. Metals like iron, zinc, copper and aluminium are extracted from their ores. Gold is found as a native metal. Thus, the treasure of different metals is hidden in rocks.
A gemstone is a mineral which is especially beautiful and rare. Gems and precious stones like diamonds and rubies are also found in rocks. Diamond is the hardest known naturally occurring substance. Talc is one of the softest minerals.
Apart from all these, the rocks contain other useful minerals. These minerals make the soil fertile. Minerals like nitrates, phosphates, sulphates and potassium salts are used as fertilizers. They ensure a good yield of crops.
Petroleum
Petroleum is a valuable mineral oil found in rocks underground. Huge petroleum oils are found under the sea.
It is believed that petroleum was produced millions of years ago by the bacterial decomposition of animals and plants which were buried underground to great depths in the earth’s crust. From petroleum, we get petrol, kerosene oil, diesel oil, paraffin wax, vaseline and lubricating oils.
New Words
Basalt: Type of dark rock of volcanic origin.
Cathedral: Main church of a district
Chalk: Type of soft white rock used for burning to make lime.
Gemstone: Precious or semiprecious stone before cutting into shape.
Gneiss: Coarse-grained rock of quartz, feldspar and mica.
Granite: Hard, usually grey, stone used for building.
Igneous rock: Rock is formed when molten magma cools and solidifies.
Limestone: Type of rock, especially composed of the remains of prehistoric plants and animals.
Magma: Liquid molten rock in the earth’s mantle and crust Marble: Type of hard limestone used, when cut and polished for building and sculpture.
Metamorphic rock: Rock that has been changed by great heat and pressure underground.
Mineral: A naturally occurring substance found in earth’s crust; for example, rock and metal.
Ore: Rock, earth, mineral, etc., from which metal can be obtained easily and economically.
Pebbles: Small stones made smooth and round by the action of water.
Quartz: A hard mineral, especially crystallized silica. Rock-salt: Common salt as mined in crystal form.
Sandstone: Rock formed of compressed sand.
Sediment: Matter that settles to the air bottom of a liquid.
Sedimentary rock: Rock is formed when fragments of material settle on the floor of a sea or lake in layers and are cemented together over time.
Shale: Type of soft rock that splits easily into thin pieces.
Slate: Type of blue-grey rock that splits easily into thin flat layers.
That’s all about Rocks and Minerals Class 5 EVS Chapter Notes. Hope you get your answers. Do share your views about this post in the comment section below.
Leave a Reply